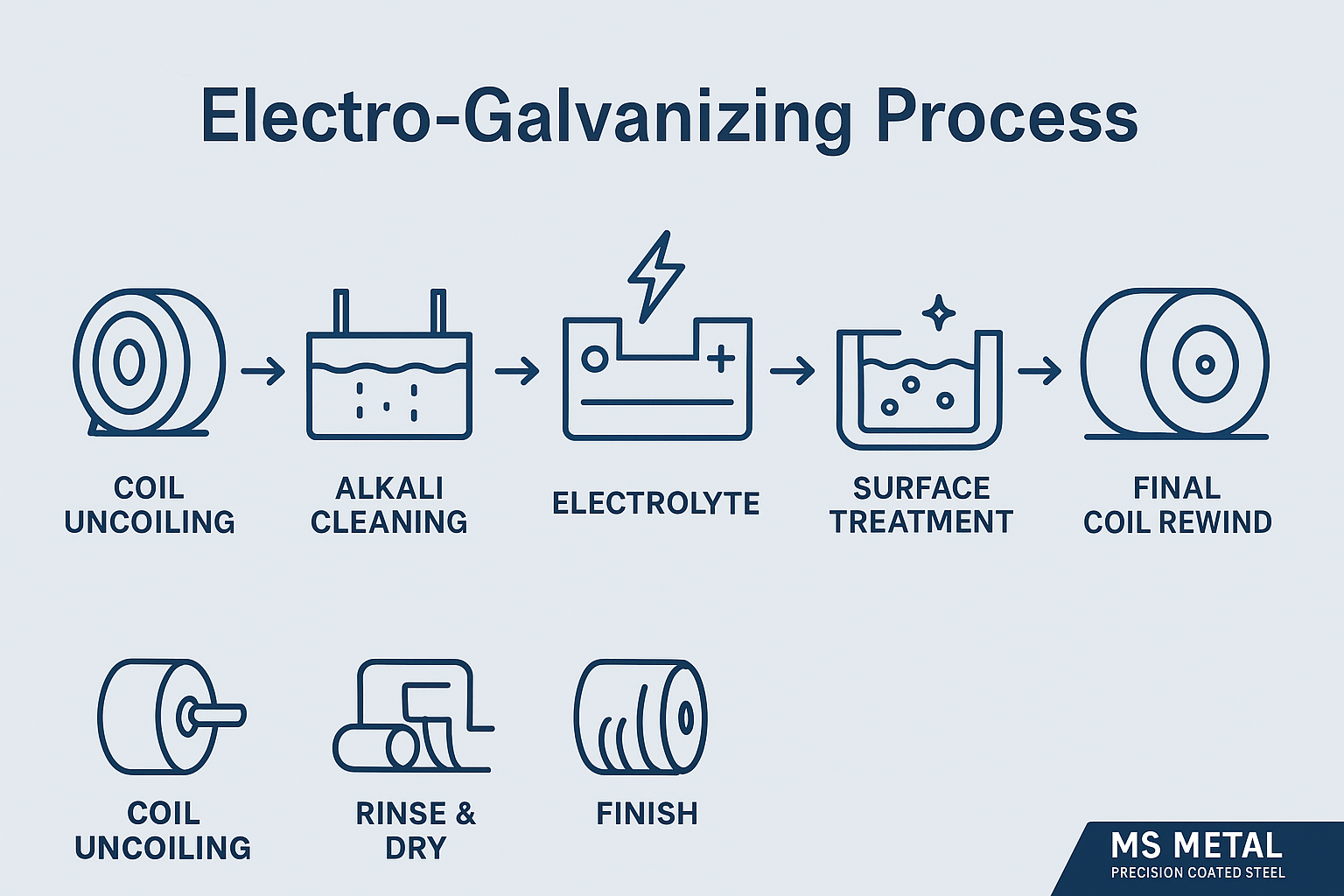
Electro-galvanized steel, commonly abbreviated as EG, is produced by depositing a thin, uniform layer of zinc onto cold-rolled steel through an electrochemical process. The EG method uses electrical current to control coating thickness with exceptional precision. This results in a cleaner, smoother surface finish.
The production of EG steel begins with cold-rolled coils that undergo thorough cleaning to remove oils, residues, and oxides. The steel then passes through an electrolytic bath containing zinc ions. When an electric current is applied, zinc particles bond to the steel surface in a controlled, microscopic layer. Because the process is continuous and tightly regulated, the resulting coating is extremely consistent across the entire sheet, After plating, the steel is rinsed, dried, and treated with anti-fingerprint or chromate coatings to further enhance corrosion resistance.
The electro-galvanized coating is a pure zinc layer that adheres to the steel through electrochemical bonding. This produces a highly uniform coating with exceptional surface flatness and brightness. The absence of alloy layers makes EG ideal for forming and deep-drawing applications because the coating remains ductile and less prone to cracking during bending or stamping operations.
One of the strongest advantages of EG steel is its superior surface quality, making it the preferred substrate in automotive panels, electrical enclosures, and appliances. The pure zinc layer enhances corrosion resistance while remaining compatible with welding and painting processes. Because the coating thickness is adjustable, manufacturers can balance cost and performance for specific uses. In environments that require consistent paint adhesion or intricate forming, EG outperforms its hot-dip counterparts.
The zinc coating is generally thinner than GI coatings, so long-term outdoor corrosion resistance is lower unless additional painting or protective layers are used. EG is also more expensive due to the precision of the electroplating process and the high-quality cold-rolled substrate required. For heavy industrial or highly corrosive environments, EG may not be the best choice unless paired with a robust paint or coating system.
Common Applications
Electro-galvanized steel is widely used in automotive body panels, electronic housings, office furniture, metal cabinets, precision components, and any application requiring high surface quality combined with moderate corrosion resistance. Its uniformity and clean appearance make it popular among manufacturers who value consistency and formability.
| Property | GI (Hot-Dip Galvanized) | EG (Electro-Galvanized) |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Method | Molten zinc dipping | Electrolytic plating |
| Coating Thickness | Moderate to very high (Z120–Z275+) | Thin and controlled (typically ≤10µm) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent outdoors | Good indoors / mild environments |
| Surface Smoothness | Rougher, spangled appearance | Very smooth & paint-friendly |
| Weldability | Good | Very good |
| Paintability | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Uses | Roofing, outdoor structures, guardrails | Automotive panels, appliances, electrical |
 MS Metal Supplies Sdn Bhd
MS Metal Supplies Sdn Bhd